In recent years, more and more residents both in Greece and abroad choose to live in prefabricated houses.
The steps that have been taken in the technology of construction and architecture are enormous. This ongoing evolution is also proven by the numerous – of excellent quality and aesthetics – prefabricated projects we see today.
Despite the above, the myths surrounding prefabricated houses continue to exist – of course, in a quieter intensity than before – and citizens’ questions are increasing.
Let’s look at the #4 most frequently asked questions about Prefabricated Houses.
#1 How are prefabricated houses made?
As is the case with all types of construction, so for Prefabricated Houses, all European and domestic laws and rules as well as architectural developments and technological requirements are followed.
Masonry
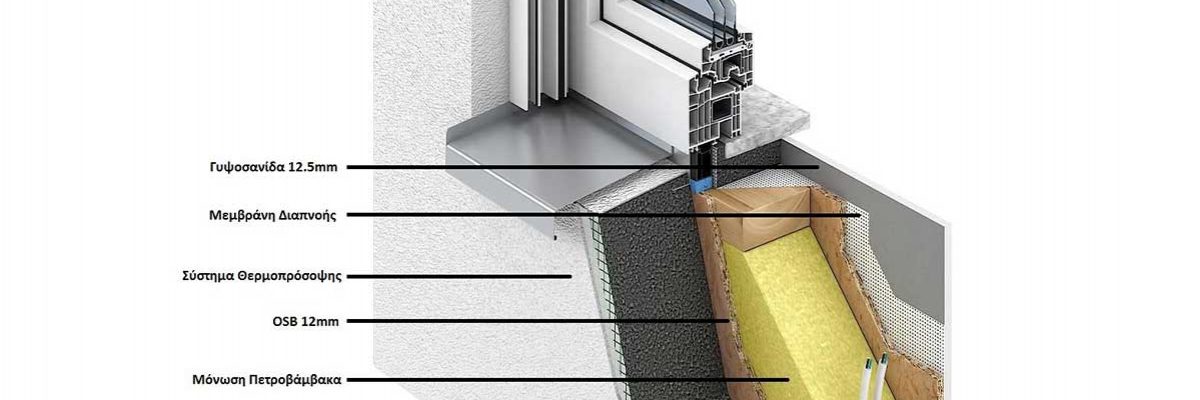
At Prokat Karagiannakis, we have ensured that the external masonry of all our constructions consists of a wooden frame – certified imported timber – a static study base of cross-section 10x5cm with insulation in between as thick as the final frame.
11mm thick OSB, 5.00cm thick EPS 100 expanded polystyrene with mechanical support and special acrylic glue are placed outside the frame.
The external surface of the masonry is plastered with a basic coating, where a special anti-alkali mesh is incorporated for absolute protection against cracking.
Finally, a final coating of fiber-reinforced inorganic material is applied.
11mm thick OSB and 12.50mm thick KNAUF gypsum board are screwed inside the frame.
As for the internal masonry, it consists of a wooden frame with mineral wool insulation in between as much as the thickness of the final frame 10cm and 11mm thick OSB plates and 12.50mm KNAUF plasterboard are placed internally and externally.
In fact, we make sure that the masonry of our prefabricated houses is constructed in a way that allows the owner to add a floor in the future.
Roof or Terrace
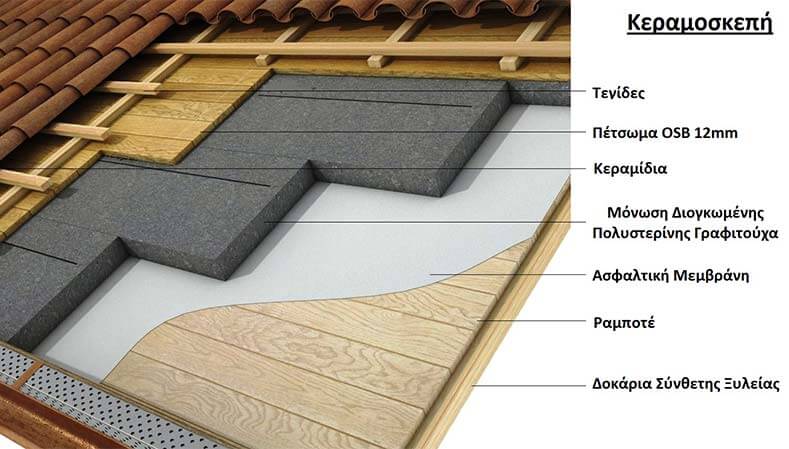
The entire house is internally reinforced with composite Swedish Timber beams, while 12mm thick OSB or batten, asphalt membrane, 2-layer insulation, and double purlins for ventilation. Finally, Roman tiles are added.
Of course, it is possible to create a flat roof in order to create a terrace.
Manufactured in the Factory
The fact that the masonry is manufactured in the factory is an advantage over conventional houses since in this way the technical failures and imperfections that arise due to on-site construction on the plot are minimized.
Plumbing & Electrical Installation
At this stage, all the appropriate placements and connections are made, so that your Prefab Home does not lag behind in anything.
Equipment
The final stage involves the equipment of the residence so that the Prefab House is ready to welcome its owner for immediate installation.
#2 Do you need a building permit for the construction of a Prefab House?
The quick answer to the above question is “Yes”.
As with traditional houses, so also with prefabricated houses, a file is submitted to the Town Planning Office for the issuance of the permit.
But let’s see what the building permit includes:
Topography
The topographical diagram is a comprehensive study that includes the plan of the existing state of the property and its contents in combination with the application of the institutional framework that governs the property (institutional lines, statements) and is differentiated according to its upcoming use.
Architecture study
The architectural study includes the coverage diagram, detailed plans, mapping of the existing condition, and technical description of the location and area of the plot.
Static Anti-seismic Study
The anti-seismic study includes an indicative control of the soil in the construction area and if deemed necessary, drawing up specifications for the preparation of a geological and geotechnical study.
Energy-Efficiency Study
The energy-efficiency study of buildings aims to improve performance, ensure energy benefits and improve comfort conditions by applying integrated energy planning.
#3 Prefabricated or Conventional House?
It is particularly important to emphasize that Prefab Houses today are not at all inferior to conventional houses and should not be confused, in any case, with the prefabricated houses of the past that were made of sheet metal.
The real difference between prefab houses and conventional ones is that in the former the structural elements of which they are composed are connected to each other with screws or oxygen welding.
The building materials used in prefabricated constructions can be either heavy, such as concrete, or light, such as wood or sheet metal.
Therefore, Prefab Homes are of the same high standard as conventional houses, but also offer a multitude of options and solutions, such as pre-determined construction costs, fast delivery time, and the possibility of immediate installation, which give them added value compared to traditional conventional houses.
#4 Do Prefab Homes have a problem with humidity?
This question is particularly interesting since it arises from the myth that follows Prefab Homes in general.
Prefab Homes have solid foundations made of cement, frame, insulating materials, aluminum, and more.
They are all certified constructions and guarantee sound insulation, moisture protection, and everything provided by law and building regulations.
At Prokat Karagiannakis, we have the experience and know-how to create prefabricated homes of high quality and aesthetics.
Contact us for your Project.